We will continue to understand nature in the elementary form which is the very essence of quantum mechanics, so we will concentrate on the subatomic level. I found that it is a good idea to read the previous article quickly before reading the current article. It gives a certain sense of continuity; however, this may not be in all cases.
There was a constant search for smaller particles in the mind of ancient philosophers and scientists even before many centuries of BC. Today scientists found that a subatomic can be decayed and create other particles. It sees particle as radiation.
In the evolution of finding the smaller and smaller particle, use of powerful particle collider helps scientist to prove their idea and imagination in real term of modern physics.
We now know that atoms are made up of three particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons — which are composed of even smaller particles such as quarks.
Hydrogen and helium were the earliest atoms in the universe. The stars were born from the clouds of gas (molecules, atoms) due to inherent interaction (force) and gravity.
Molecules are held together by the chemical bond with two or more atoms. In our discussion, we will mostly concentrate on the subatomic structure.
Fundamental particles electrons and quarks are made up of everything.
There are 4 fundamental forces of nature –
Electromagnetism
Gravitation
Strong interaction
Weak interaction
Everything in the universe is bound by these forces.
Like quark leptons are elementary particles that exist on their own. There are six kinds of leptons; electron is one of them as particle physicists find them by large collider.
The electron has various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, spin, and mass. Unlike quarks, however, an electron is not subject to the strong interaction, but it is subject to the other three fundamental interactions: gravitation, the weak interaction, and to electromagnetism.
Isotopes
The second law of Dalton says – All atoms of an element are identical. This is not true, here comes Isotopes.
Isotopes disproved Dalton’s 2nd Law. Isotopes of an element are atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Scientists found by bombarding lithium atoms with protons and splitting them into two helium atom. This disproved Dalton’s 5th Law that says atoms could not be divided, created or destroyed.
Notation
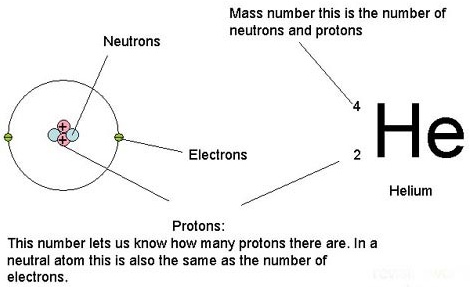
Courtesy of Google
Atomic number / Atomic mass number:
Let’s look at Carbon.
The atomic number of Helium is 2 (number of protons)
Each atomic number identifies a specific element; Carbon has 6 protons so its atomic number is 6. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom’s mass number.
The mass number of Carbon is 12. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. But scientists found Carbon has mass number 13 and 14 in carbon isotopes due to extra neutrons.
Carbon 12, 13 and 14 isotopes emphasizes chemical composition.
Nuclear physics uses a term nuclide instead of isotopes, it deals with nuclear properties.
Physicists use the term Radioactive, primordial, and stable nuclide for isotopes/nuclides.
Primordial nuclides (289 types) had created in the solar system as it evolved after the big bang.
There are about 339 naturally nuclides on earth. Artificially created 3339 nuclides are currently known.
We will concentrate on the latest electron cloud model of an atom. This model explains atomic orbitals which differ from the old idea of electrons orbit (like the planets). Electrons do not go in a circle, it has a very complex movement. An atomic orbital describes a region of space (electron cloud) in which there is a high probability of finding the electron. Four types of Orbitals are very important, whose scientific notation are s, p, d and f (sharp, principle, diffuse and fundamental).
Why atom are bound together. All 4 forces are playing together to stay a stable atom.
An electron has an orbital motion which creates centrifugal force and counteracts with force of attraction (electrostatics) from the proton.
Protons having positive charge should repel each other due to electrostatic force, but in reality, they held together due to strong nuclear binding force. Further study of Nuclei indicates that they are held together by the formation of nucleon spin pairs and thereby creating an attraction between neutrons and protons.
For now, our discussion will be limited to electron shell and its notation.
Levels, Sublevels, Orbitals, and Electrons
Electronic shells (orbits) are related to their energy level. The electron jumps from one level to another level due to extraneous energy.
Huge empty space of an atom is divided into regions called principal energy levels, numbered 1, 2, 3, 4,… from the nucleus.
The levels can be broken down into sublevels. They are s, p, d, and f sublevels.
The sublevels contain orbitals. Orbitals are spaces that have a high probability of containing an electron.
The maximum number of two electrons can be in one orbital.
Sublevel ‘s’ has 1 orbital, sublevel ‘p’ has 3 orbitals, sublevel ‘d’ has 5 orbitals and sublevel ‘f’ has 7 orbitals.
Level 1 has s sublevel. Level 2 has s and p sublevel, Level 3 has s, p, and d. Level 4 has s, p, d and f sublevels.
So each principal energy level can contain up to 2n2 electrons, where n is the number of the level.
So level 1 has 2, level 2 has 8, level 3 has 18, and level4 has 32.
Only seven energy levels are needed to contain all the electrons in an atom of any of those elements now known as of today.
The notation used to describe an atom for elements as follows:
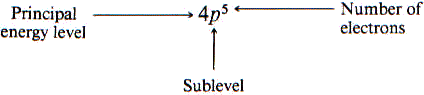
Electrons are positioned according to lowest energy sublevels first from a nucleus in order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p …..
Electron Configuration – shorthand notation for showing what sublevels are filled-
- Carbon atom has 6 electrons – 1s2 2s2 2p2 because 2+2+2=6
- Silicon atom has 14 electrons – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 because 2+2+6+2+2=14
By nature electrons are filled according to lowest energy sublevels first.
Electron Cloud Model: –
It is the most recent model of the atom as defined by quantum mechanics which takes into consideration of probability/uncertainty physics, math, and wave theory.
Path of the electron orbit is not a simple circular orbit. It is an extremely complex path; scientists defined this path as a cloud around the nucleus.
Particle Physics:
Study of atomic and subatomic particle continues throughout the twenty century. Contribution from Einstein and many other scientists are enormous. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory about nature. It describes the behaviors of particles and their interactions in a probabilistic manner. Particle physics uses quantum mechanics to predict possible interaction outcomes with known and hypothetical particles.
The door opened for modern particle physics by Satyendra Nath Bose is so enormous that we still don’t know its real impact. His theory with mathematical formulation is known as “Bose-Einstein condensate”. It took 75 years to prove his theory in the laboratory in 1995.
Bose wrote a short article called “Planck’s Law and the Hypothesis of Light Quanta” and submitted to the Philosophical Magazine. However, the paper was rejected.
Then Satyendra Nath Bose wrote to Einstein, sharing his insights about an existing physical law describing how light and matter interact. Bose wrote to Einstein “Though a complete stranger to you, I do not feel any hesitation in making such a request” ….. Bose wrote. “We are all your pupils though profiting only by your teachings through your writings”.
Bose described a new approach to analyzing particles like photons. Einstein helped get Bose’s work published.
Bose and Einstein extended the idea to atoms and this led to the prediction of the existence of phenomena which became known as Bose-Einstein condensate, a dense collection of bosons (named after Bose).
Fundamental particles
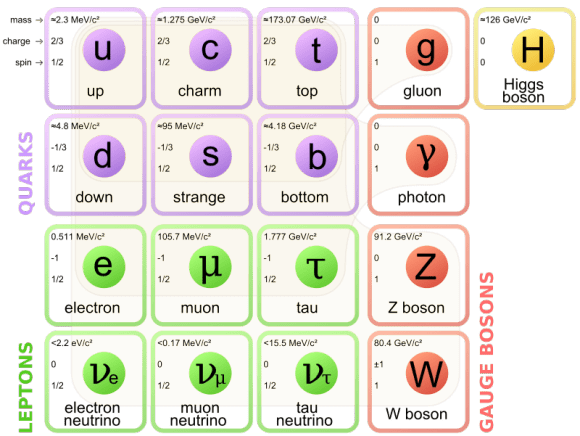
Courtesy of Google
















Comments »
No comments yet.
RSS feed for comments on this post. TrackBack URL
Leave a comment