Classical physics took a huge leap orchestrated by Sir Isaac Newton with a better grasp of Calculus and gravitational constant, subsequently, probability, advanced calculus, and many new branches of physics such as Thermodynamics, electricity and Statistical physics showered humanity with invaluable knowledge.
A child danced with joy when he spotted a rainbow on the freshly rainy sky. Young Newton observed that when light passed through a prism, it dispersed in various colors. Why colors are so different? This was then a million-dollar question to the scientists. Answer to this opens the doorway to quantum physics. The answer came a lot later.
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb (14 June 1736 – 23 August 1806) who is known by his eponymous Coulomb’s law; this was where the idea of quantification had embarked for electromagnetic phenomena. Contribution from Michael Faraday (22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) and other scientists and physicists are the foundation of modern physics.
James Clark Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a pioneer in the theory of electromagnetism. Einstein described his work as the most profound work physics has experienced since the time of Newton. Maxwell’s equations for electromagnetism have been called the “second great unification in physics”.
Scientists from ancient times look keenly into the magnet, light, and, the electrostatic phenomenon as a unique source of energy and developed theory on each subject matter. With the advancement of classical physics, the theory of electromagnetism started to believe that all these natural behavior are actually a manifestation of the same energy that wrapped electricity, magnetism, and light and ushered the era of modern physics by planting the seed of modern and quantum physics.
In 1865, James Clark Maxwell revealed that electric and magnetic fields travel through space as waves moving at the speed of light with different frequencies and wavelengths. And this is true for all electromagnetic waves. This brought a renaissance in modern physics. Visible sunlight and all other electromagnetic waves and their electric and magnet component of field travel at a constant speed (3 times 108 meter/sec). It obeys a simple equation V= f λ, where V is velocity, f is frequency and λ is the wavelength. The energy of the field increases with frequency. Both standing electric and magnetic waves are 90 degrees out of phase, and the magnitude of the magnetic component is much smaller than the electric component.
Typically, human eyes can detect wavelengths from 380 to 700 nanometers. Everything in the universe radiates with its own internal heat and temperature. Some of you have seen how the color of the metal changes as it melts in the smithy shop, and this color change is due to the temperature of the steel. Our body temperature is low so you and I emit in the IR region and invisible to our eyes. Log burns in a fireplace or out in the field while camping, log burns and emits various colors on log surface (not confused by flame color). Why colors are so different? Scientists determined it is due to the different frequencies or wavelengths. The highest frequency is cosmic, then gamma, … and so forth, such as x-ray, UV ray(burn), visible light(see), infrared (heat effect)… microwave.. shortwave, longwave as frequency decreases. As fire log stops emitting light, you can still feel radiated heat with IR and not visible by our eyes. However while the fire log starts to burn, its temperature rises, and visible color of light appears on the log surface, and eventually flame starts.
What is happening? – Heat energy wave hits the atom; atom oscillates and emits electromagnetic radiation. James Maxwell understood the charged particle and its electromagnetic aspect of the radiation. He and other scientists plotted a curve from the experiments which is as shown below:
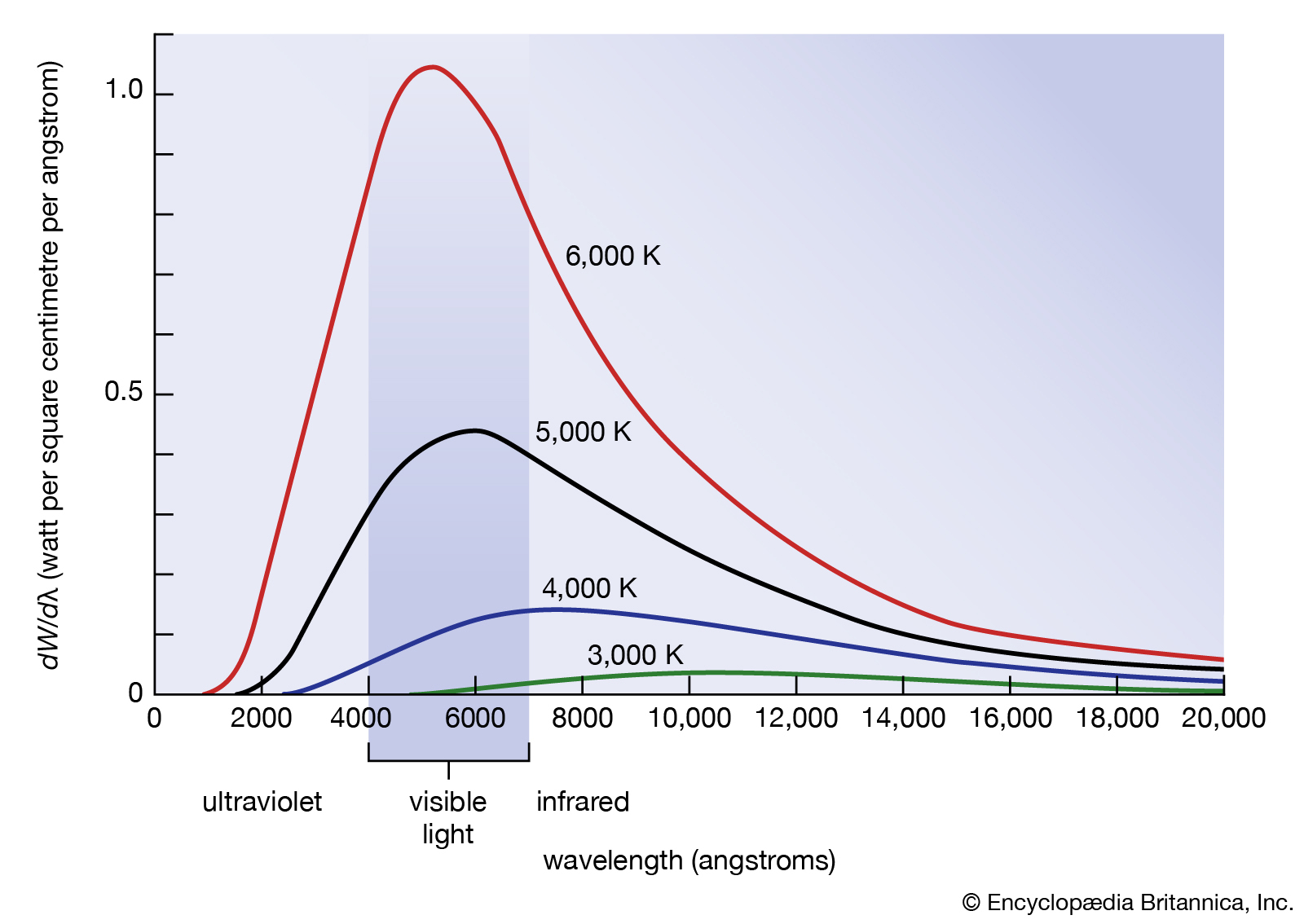
Courtesy of Google
Actually, all forms of light and energy are part of the same phenomena. Our eyes can detect only a small amount of this energy, that portion we call “visible light.”
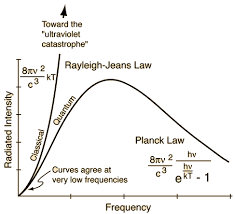
From Blackbody radiation and analysis of UV catastrophe Plank law gave the idea of quantization of energy, Einstein and Plank conceptually realize energy comes in a packet, and each packet of energy called a photon, the carrier of electromagnetic wave, and it can’t be more than energy (kT) where k is Boltzmann constant.
Photoelectric
Who else can visualize that light is made of small particle called corpuscle other than Newton (1642-1727) but about the same time Huygens (1629-1695) hypothesized that light is a wave? Experimented with double slit, Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) proved Huygens’s lightwave idea. Scientist’s community had accepted light as wave only until Eisenstein proved it is a particle called photon but with a twist that it is both particle and wave.
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) experimented and conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves as predicted by James Clerk Maxwell. His name (Hertz)is used for the unit of frequency.
In 1887 photoelectric effect was laboratory tested, when UV light on a metal ejected an electron. It proved only after the minimum energy of light an electron was ejected. Thus an electron can be dislodged from the binding force of an atom thereby from the molecule by light energy. This made a revolution in physics and modern/quantum physics was born. It proved that each photon has an energy equivalent of hf quantity. Where ‘h’ is plank constant. So light is behaving as particle and wave. There is no more disagreement in the scientific community.
Electron was always considered as a particle. De Broglie (15 August 1892 – 19 March 1987) in 1924 postulate that electron (particle) had wave characteristics similar to a photon. Thus everything in the universe can be viewed from wave/frequency.
Davission(October 22, 1881 – February 1, 1958) and Germer (October 10, 1896 – October 3, 1971) in 1927 proved electron is a wave by double-slit experiment with an electron. So they proved that electron is also wave and thus it proves the De Broglie postulate. So all objects including us have wave characteristics.
Here is a background simple math behind it:
Knowing E=mc2; E=h f; c = f λ; m=E/c2;
So, momentum is p= (m v) = E/c ; as v = c(light) or E=pc;
P= h/λ; Momentum of light is plank constant/wavelength
De Broglie extended for electron
λ = h/p=h/mv; m being mass of electron;
Knowing from coulomb theorem – energy E=q V; where q is charge and driven by V voltage.
Charge of an electron can be written as e = 1.6 times 10-19 coulomb
Classical definition of energy as E =1/2mv2 (v = velocity); Charge of electron q=e;
So, eV = 1/2mv2; we can derive the equation of wavelength λ=h/ ;
It is true all objects have wavelength but practically they are not measurable.
All the modern principles need the use of plank constant for their mathematical understanding.
Heisenberg uncertainty principle, De Broglie wavelength (as shown in simple math above), Schrodinger equation, Energy levels of electron orbits, Relation between energy and frequency of a photon.
Plank constant is 6.63 times 10-34 Joule second.
Photon can’t have enough energy than what is available, available is E = kT.
These are the basic understanding of the wave-duality of nature. It seems a better understanding of e=mc2 and De Broglie postulate, and subsequently, Heisenberg uncertainty principle and Paul Daric positron and wave equation derived by Schrodinger will allow us for the good mathematical background of wave-duality. So keep moving.
Classical physics with statistical thermodynamics could not prove experimental radiant energy, in 1900 Max Planck postulated that the electromagnetic energy is not continuous, but discrete. Planck’s Law is defined; see the equation below, where h=6.62 x 10-34 is the Planck’s constant. Light is emitted in quants and can be considered not only as a wave-like entity but also as a particle, or photon, with the energy given by the PlanckEinstein relation
















Comments »
No comments yet.
RSS feed for comments on this post. TrackBack URL
Leave a comment