Publication 6 – Magnet & Electric fields and interaction of fields.
Did you read Publications 1 through 5? If not, please take a moment to read those sections. I am trying to walk through the basic understanding of the physics. Modern physics requires a good understanding of mathematics. At this time we will ignore all the complexity of mathematical formulation. I use content from Wiki, and lot of discussion from Quora regarding the subject. I tried to filter out the complexity, so that my writing is simple enough for the general public, young and adult,
Physics in micro level deals by Quantum mechanics, quantum physics, or quantum theory.
“Dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter” is very difficult to comprehend as it needs to understand mathematical expression as provided by Quantum mechanics.
Before we analyze particle in micro level and wave-like behavior we should try to understand basic of Magnet, Magnetism, electricity, photoelectricity and some basic understanding of interrelationship and mathematical formulation.
Magnet and Magnetism:
Ancient people learned about magnetism from lodestones. Greece, India, and China knew magnet around 2500 years ago. Do you know – in ancient time Indian medical used to use the magnet to remove arrows from the body? Magnetic compasses were used in navigation in 12 century, compass works due to earth magnetic field.
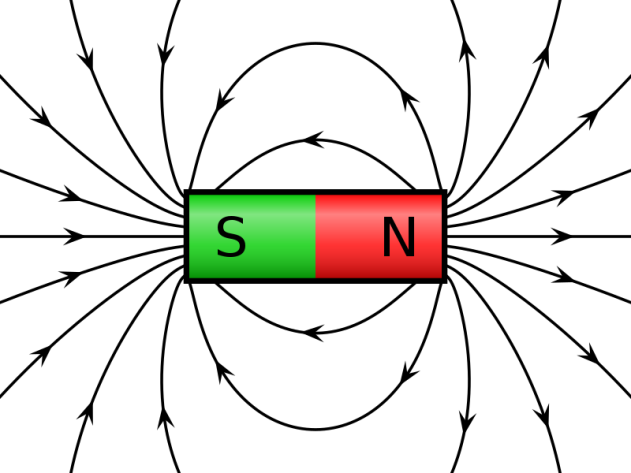
We saw the above picture in Physics book. This kind of magnetic field is not visible by eye, but they are lab tested; the field is due to energy; this field is the most powerful force in nature. Earth’s rotation and heated molten core contribute the magnetic behavior.
The electromagnetic field is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. The other forces are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction. The electromagnetic interaction/field extends indefinitely throughout space.
This EM field is very important to our everyday life; let us concentrate on this subject. EM is composed of ELECTRICAL and MAGNETIC field. The electric field is produced by stationary charges and the magnetic field by moving charges; to study further we will look into Maxwell and Lorentz theory where it gives the idea how charges and currents interact with the electromagnetic field. The force created by the electric field is much stronger than the force created by the magnetic field.
Classical Physicist and scientist started to view the electromagnetic field as a smooth, continuous field, propagated in a wavelike manner; with the progress of quantum field theory, the field is also viewed as being composed of individual particles.
An understanding of the relationship between electricity and magnetism began in early 1800. André-Marie Ampère found that the magnetic field circulating in a closed-path was related to the current flowing through the perimeter of the path;
Michael Faraday found that a time-varying magnetic flux through a loop of wire induced a voltage.
James Clerk Maxwell linked into Maxwell’s equations, unifying electricity, magnetism, and optics into the field of electromagnetism.
Understanding Electromagnetism has continued into the 21st century, linking with fundamental theories of gauge theory, quantum electrodynamics, electroweak theory, and finally the standard model.
In a nutshell, the fundamental idea is “The source for electric field is an electric charge, charges in motion results in a current, thereby causes magnetic field”.
Now let us look a little bit closure to the physics with their mathematical findings. However, we don’t need to go in-depth of derivation and formulation.
Lorentz force and Maxwell’s equations –
The Lorentz force law describes the force acting on a moving point charge q in the presence of electromagnetic fields.
The Lorentz force law (electromagnetic force) describes the effect of B (magnetic field), E (electric field), upon a point charge, but it did not take consideration of other forces namely gravity and nuclear force.
Maxwell’s equations describe how electrically charged particles and currents, or moving charged particles give rise to electric and magnetic fields, it links with all other forces
Magnetic field
The magnetic flux density B is a vector field.
Magnetic moment
A magnet’s magnetic moment or magnetic dipole moment μ is a vector; it characterizes the magnet’s overall magnetic properties.
A wire in the shape of a circle with area A and carrying a current I has a magnetic moment of magnitude equal to IA.
Lorentz force –
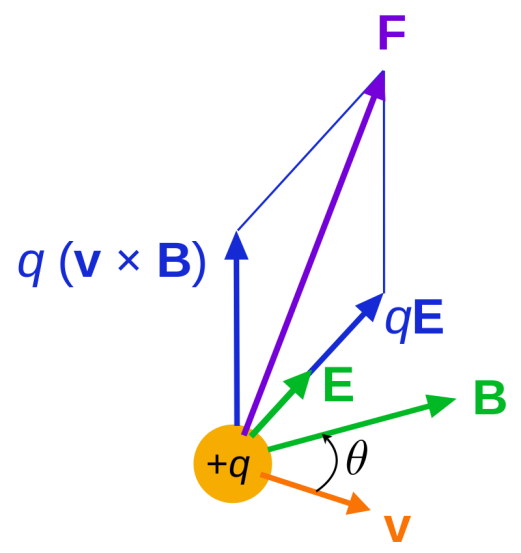
The classical formula consists of B (magnetic field), E (electric field), v (velocity), and q (charge) as input to derive the F (force).
Thus the electromagnetic force F on a charge at a given point and time is a certain function of its charge q and velocity v, which can be parameterized by two vectors E and B, in the functional form:
F = q (E + v B)
The fields are true everywhere in space and time.
Courtesy of Google
Lorentz force F on a charged particle of charge q in motion with velocity v. The E field and B field vary in space and time.
Maxwell’s equations:
Effects of electromagnetism are every part of our life including bio-science, as well as Outer Space,
These very complex set of partial differential equations are the foundation of classical and modern electromagnetism. It is the mother of a mathematical model for electric, optical and radio technologies, power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc.
Maxwell’s equations demonstrate how fluctuating electric and magnetic fields propagate at the speed of light. We call them electromagnetic radiation, these waves may occur at various wavelengths to produce a spectrum from radio waves to gamma-rays. It proves that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon.
Frankly speaking, all the equations are not the scope of the publication. Readers who are interested in Maxwell’s equation may go through further study of higher physics.
Since my knowledge is limited I will go through some basic understanding and write basic concept and show some equations for completeness, but no need to go in depth.
I repeat that all the following equations are just for completeness, you may ignore now. We will come back in the future publication for more understanding.
Maxwell’s equation covers Gauss’ law, Gauss’s law for magnetism, Maxwell-Faraday, Ampère’s law with Maxwell’s addition.
Let us try to understand the basics of the above laws.
Gauss’s law for electricity
The field lines begin at positive electric charges and end at negative electric charges. The net outflow of the electric field through any closed surface is proportional to the charge enclosed by the surface.
The number of field lines passing through a closed surface calculates the total charge enclosed by that surface.
Formulas – Courtesy of Wikipedia
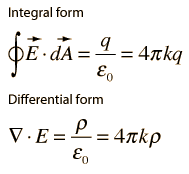
Gauss’s law for magnetism
Gauss’s law for magnetism states that there are no “magnetic charges, analogous to electric charges”.
The net magnetic flux out of any closed surface is zero.
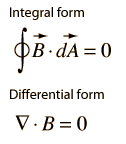
This equation states that magnetic field lines neither begin nor end but make loops or extend to infinity and back. In other words, It means that the total flux of the vector field through an arbitrary closed surface is zero.
Maxwell-Faraday law of induction
The Maxwell–Faraday’s law of induction describes how a time-varying magnetic field creates an electric field.
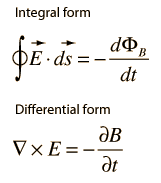
It states that the work per unit charge required moving a charge around a closed loop. It equals the rate of decrease of the magnetic flux through the enclosed surface. This aspect of electromagnetic induction is the operating principle behind many electric generators: for example, a rotating bar magnet creates a changing magnetic field, which in turn generates an electric field in a nearby wire.
Ampère’s law with Maxwell’s addition states that magnetic fields can be generated in two ways:
By electric current and
By changing electric fields. This is “Maxwell’s addition”.
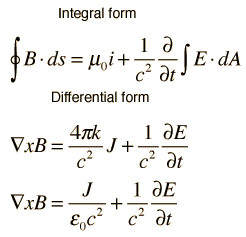
Where
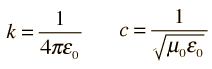
In integral form, the magnetic field induced around any closed loop is proportional to the electric current plus displacement current (proportional to the rate of change of electric flux) through the enclosed surface.
These set of equations are consistent for non-static fields, without changing the laws of Ampere and Gauss for static fields. It predicts that a changing magnetic field induces an electric field and vice versa.
“Electromagnetic waves” travel through empty space. The speed of the electromagnetic waves matches the speed of light; light is one form of electromagnetic radiation so as the others “X-rays, radio waves, and others”.
Thus it brings the connection between electromagnetic waves and light unifying the theories of electromagnetism and optics.
In the future, we will try to understand vector calculus for 3 dimensions. There will be more detail on this subject later.
















Comments »
No comments yet.
RSS feed for comments on this post. TrackBack URL
Leave a comment